Unveiling The Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide To Topographic Map Mountains
Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Mountains
Related Articles: Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Mountains
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Mountains. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Mountains
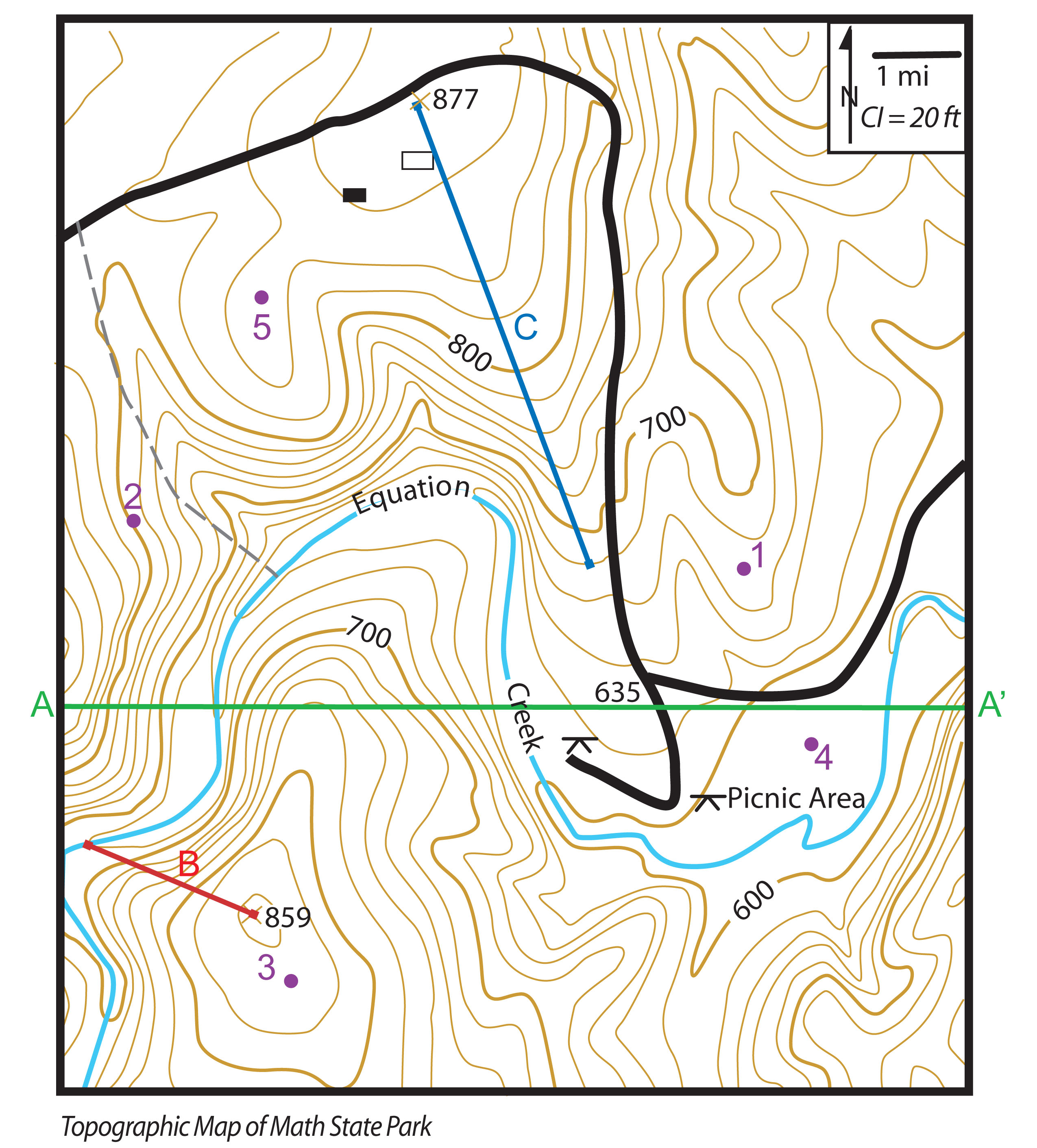
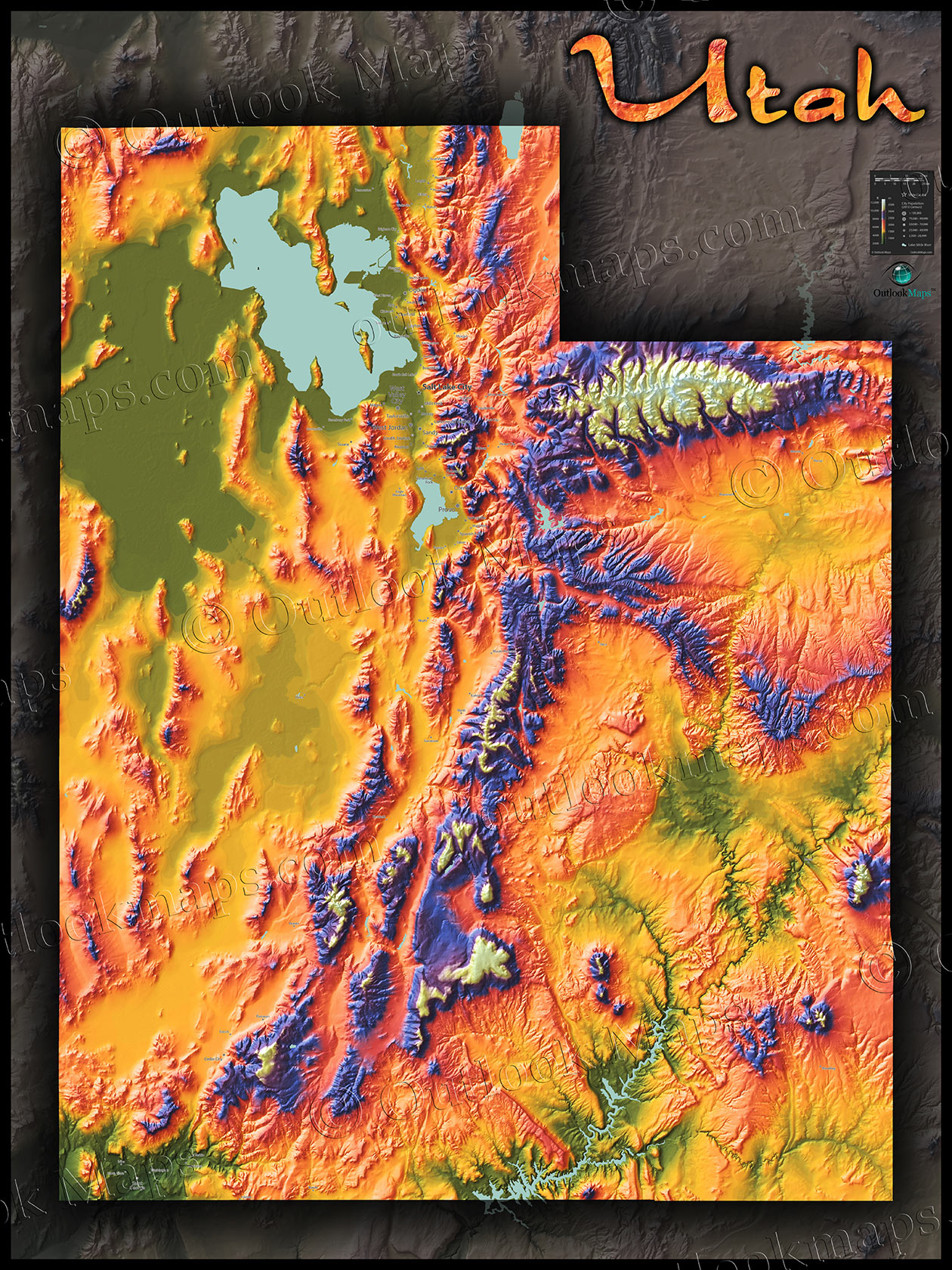
Topographic maps, those intricate representations of Earth’s surface, are more than just lines and symbols. They are powerful tools that translate the three-dimensional world into a two-dimensional representation, revealing the intricate details of our planet’s topography. Mountains, those majestic landforms that rise above the surrounding terrain, are particularly well-represented on topographic maps, providing valuable insights into their shape, elevation, and surrounding environment.
Understanding the Language of Elevation
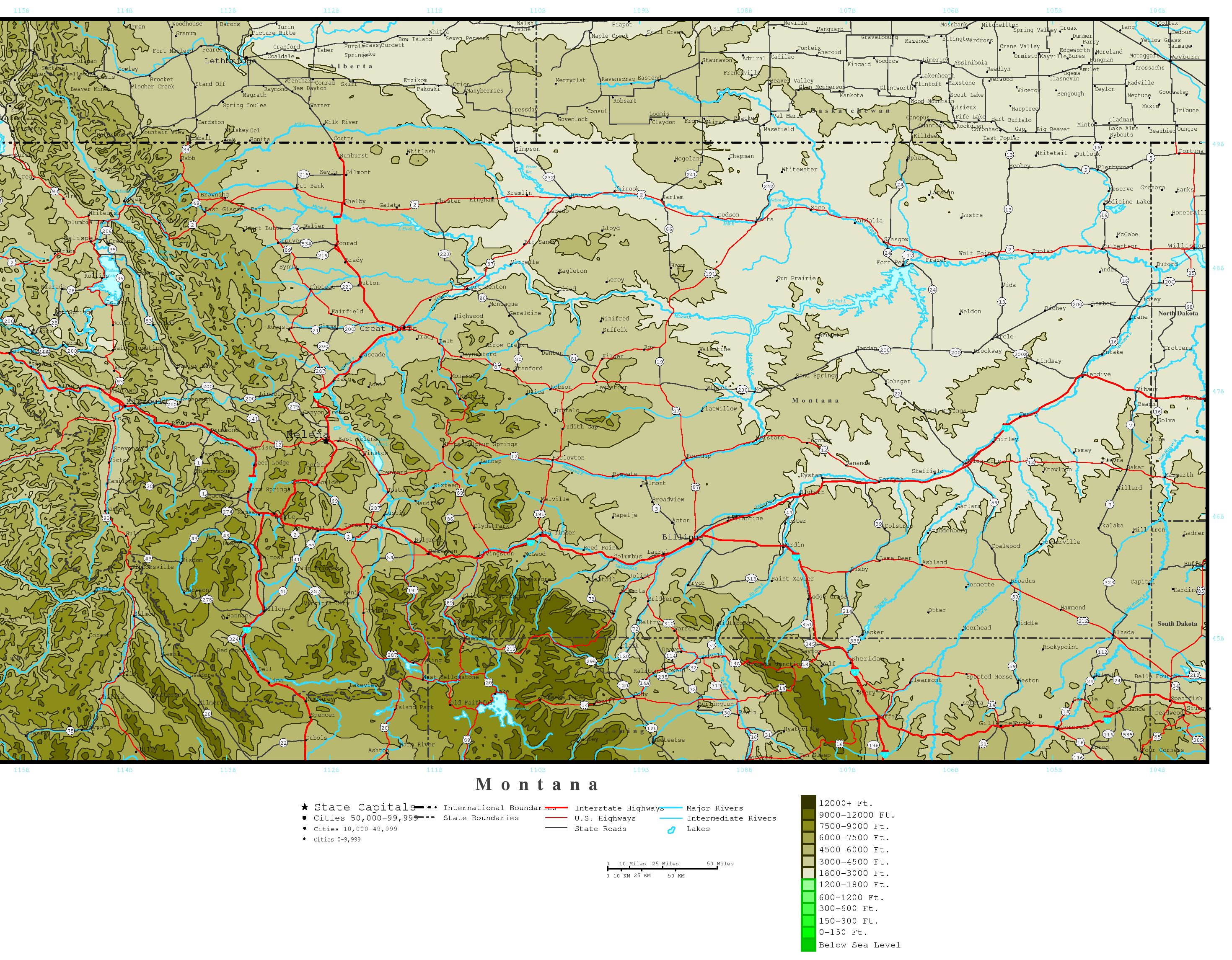
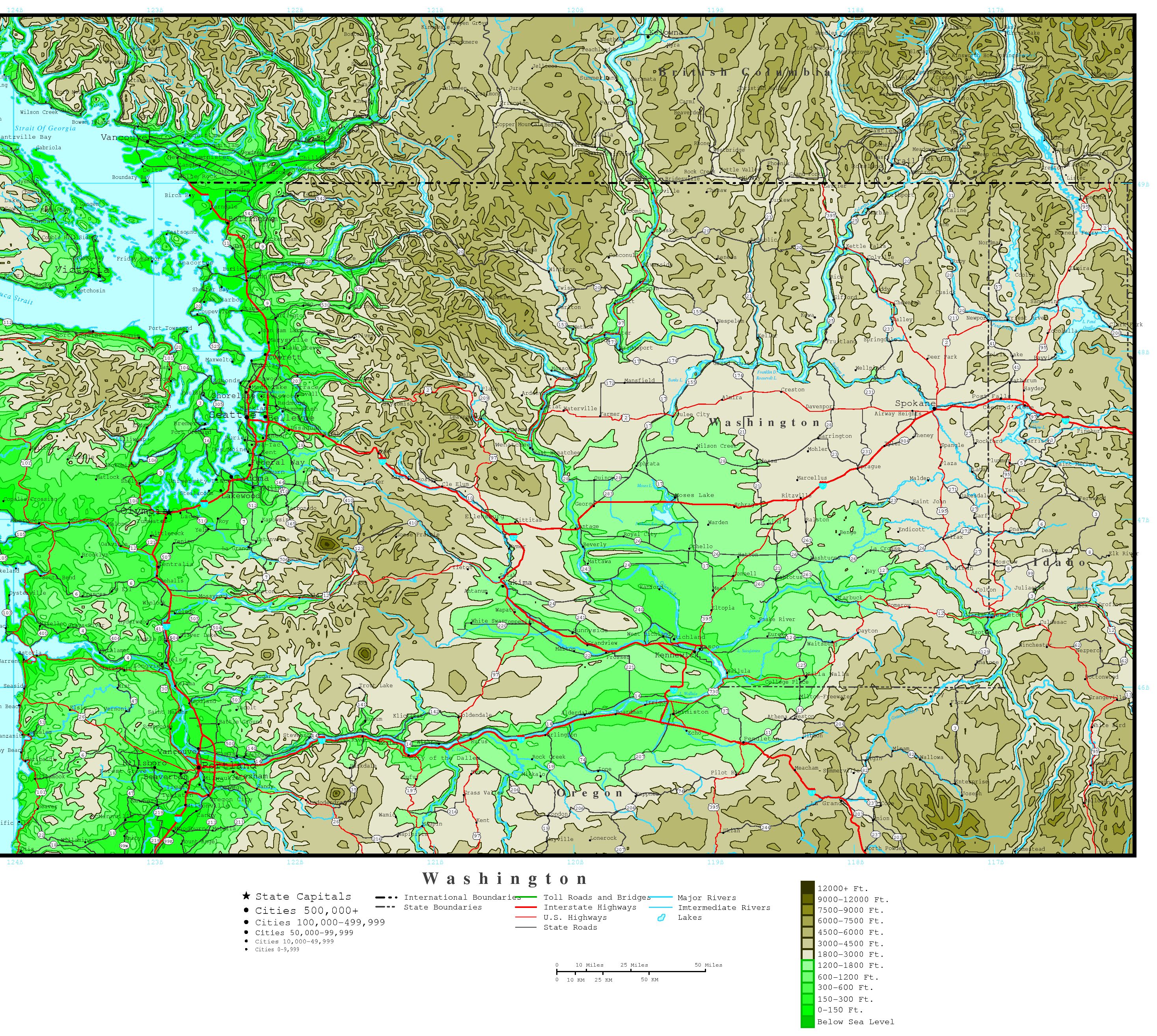
At the heart of topographic map mountains lies the concept of contour lines. These lines, often depicted in brown, connect points of equal elevation. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; the farther apart they are, the gentler the incline. This simple principle allows map users to visualize the terrain’s three-dimensional structure, revealing the rise and fall of mountains, valleys, and plateaus.
Beyond Contour Lines: Delving Deeper into Topographic Map Mountains
Topographic maps are not limited to contour lines. They employ a rich vocabulary of symbols and annotations to convey additional information about mountains and their surroundings.
- Elevation Points: Numerical values, often marked by a small triangle, indicate the precise elevation of a specific point. This helps pinpoint the highest peak of a mountain or determine the elevation of a particular pass.
- Spot Elevations: These are similar to elevation points, but they are typically used to indicate the elevation of important features like saddles, ridges, or key locations along a trail.
- Relief Shading: This technique uses shades of gray to simulate the effects of light and shadow on the terrain, adding visual depth and making it easier to discern the shape of mountains and valleys.
- Stream and River Symbols: These symbols indicate the flow of water, highlighting the presence of drainage patterns and providing insights into the erosion and geological history of the surrounding area.
- Vegetation Symbols: Topographic maps often include symbols representing different types of vegetation, offering information about the plant life found in and around mountains.
The Importance of Topographic Map Mountains
Topographic maps, particularly those highlighting mountains, play a crucial role in various fields and activities:
- Outdoor Recreation: Hikers, climbers, and other outdoor enthusiasts rely on topographic maps to navigate challenging terrain, plan routes, assess potential hazards, and estimate travel times.
- Land Management and Conservation: Topographic maps aid in land management by providing detailed information about the terrain, allowing for better planning of resource use, infrastructure development, and conservation efforts.
- Engineering and Construction: Topographic maps are essential tools for civil engineers, providing crucial data for designing roads, bridges, dams, and other infrastructure projects that may involve mountainous terrain.
- Scientific Research: Geologists, ecologists, and other scientists use topographic maps to study the formation of mountains, analyze geological formations, track changes in elevation, and assess the impact of climate change on mountainous environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the different types of mountain symbols used on topographic maps?
Topographic maps utilize various symbols to represent mountains, including:
- Contour Lines: As discussed earlier, these lines connect points of equal elevation, revealing the shape of the mountain.
- Elevation Points: These points, often marked by a small triangle, indicate the precise elevation of a specific location on the mountain.
- Spot Elevations: These are similar to elevation points but are used to indicate the elevation of important features like saddles, ridges, or key locations along a trail.
2. How can I determine the steepness of a slope using a topographic map?
The steepness of a slope is determined by the spacing of contour lines. Closer contour lines indicate a steeper slope, while wider spacing indicates a gentler slope.
3. What is the difference between a topographic map and a contour map?
While both topographic maps and contour maps utilize contour lines, topographic maps are more comprehensive. They include additional information like spot elevations, symbols for vegetation, drainage patterns, and cultural features, making them more informative for navigation, planning, and research.
4. How can I use a topographic map to plan a hiking trip?
Topographic maps are invaluable for planning hiking trips. Use them to:
- Identify potential routes: Study the contour lines to determine the difficulty of the trail and identify potential obstacles.
- Estimate travel time: The density of contour lines can help estimate the time required to navigate a specific section of the trail.
- Locate water sources: Look for symbols representing streams, rivers, and lakes to ensure access to water.
- Identify camping spots: Choose flat areas with good drainage and access to water.
5. What are some tips for interpreting topographic map mountains?
- Start with a basic understanding of contour lines: Familiarize yourself with how contour lines represent elevation and slope.
- Use a ruler or compass to measure distances and elevations: This will help you accurately assess the terrain and plan your route.
- Look for patterns in the contour lines: The shape of the contour lines can reveal the presence of ridges, valleys, saddles, and other landforms.
- Pay attention to the map’s scale: A smaller scale map may not show as much detail as a larger scale map.
Conclusion
Topographic map mountains offer a window into the intricate structure and beauty of Earth’s terrain. By understanding the language of contour lines, symbols, and annotations, we can unlock a wealth of information about the shape, elevation, and surrounding environment of these majestic landforms. Whether for outdoor recreation, scientific research, or land management, topographic maps remain essential tools for navigating, understanding, and appreciating the world’s mountains.
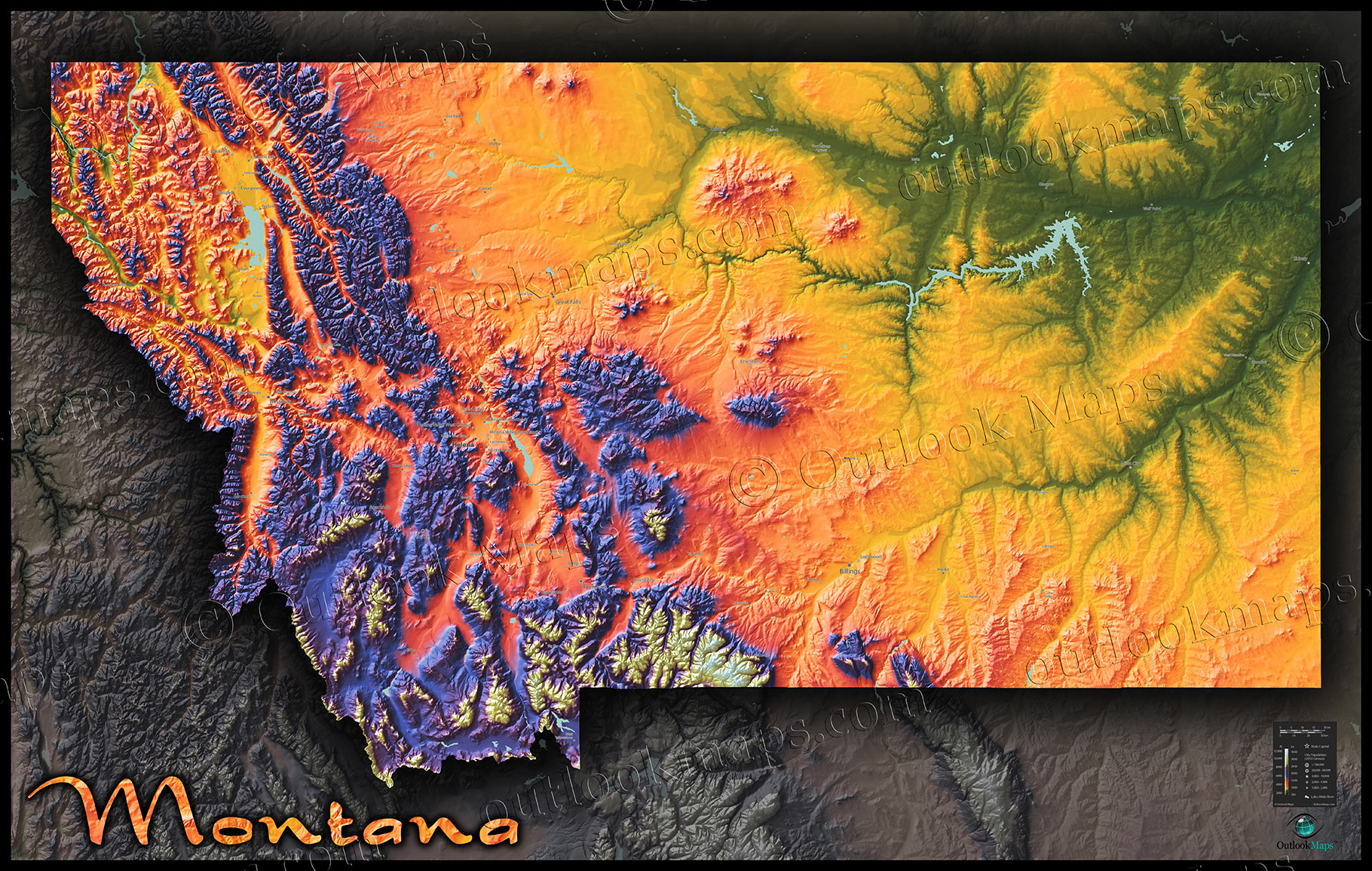
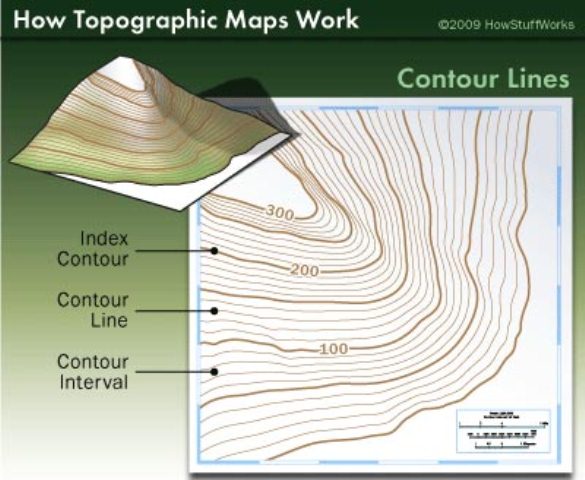

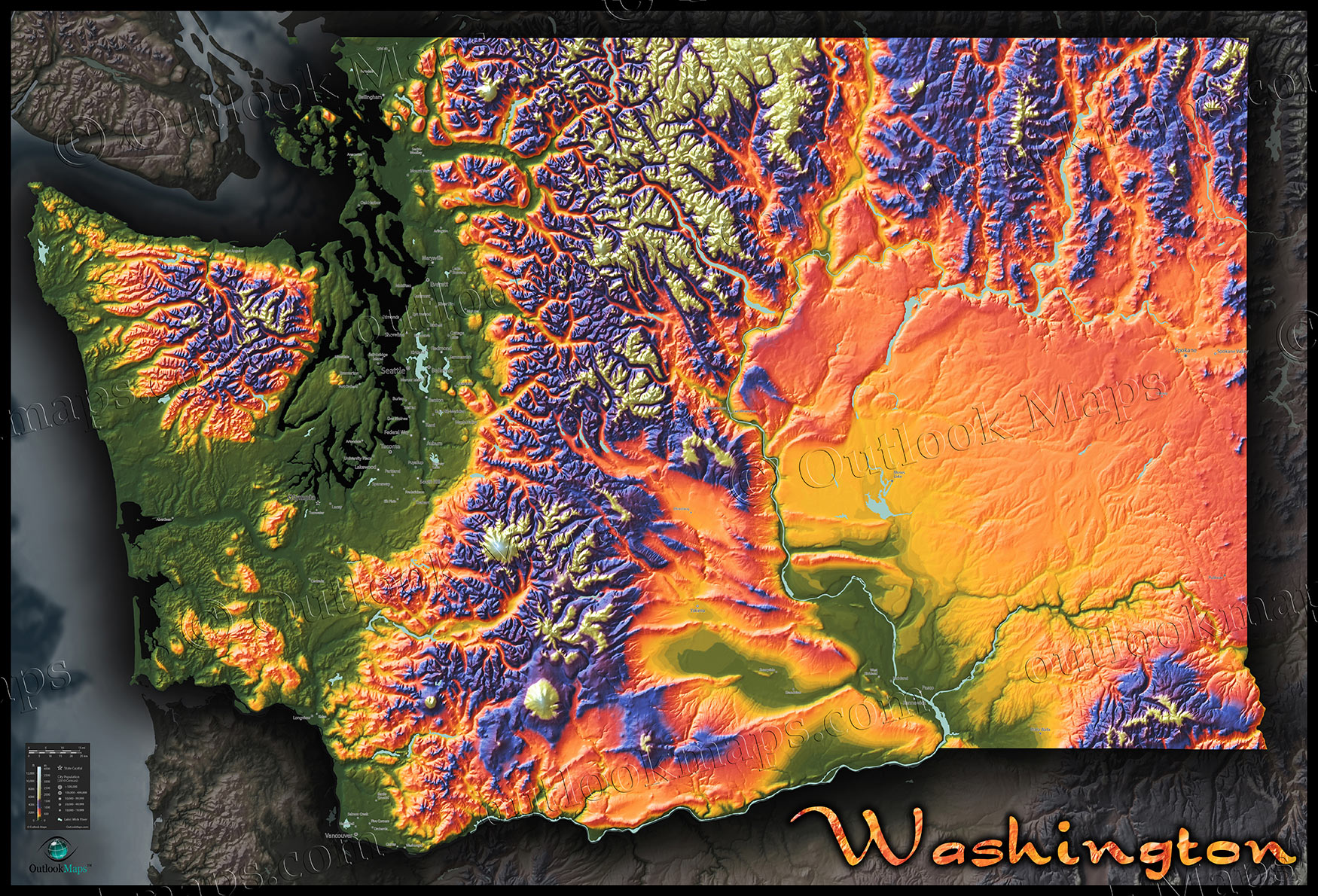

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Mountains. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Geographical Journey Through The Republic Of Congo: Unveiling A Nation’s Landscape And Potential
- Navigating Iowa’s Roads: A Comprehensive Guide To The Iowa DOT Road Condition Map
- Navigating Moreno Valley: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Layout
- The Power Of Maps: Understanding The Role Of Map Servers In The Digital Age
- Mastering The Battle Royale: The Importance Of Warm-Up Maps In Fortnite
- A Comprehensive Guide To Printable State Maps: Unveiling The Power Of Visualization
- The Missouri River: A Vital Lifeline Across The American Heartland
- Deciphering Nevada’s Political Landscape: A Guide To The Silver State’s Electoral Map
Leave a Reply