Navigating The Landscape Of Data: A Deep Dive Into Java 8’s Map
Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Deep Dive into Java 8’s Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Deep Dive into Java 8’s Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Deep Dive into Java 8’s Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Deep Dive into Java 8’s Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Deep Dive into Java 8’s Map
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of Map
- 3.2 Exploring the Key Features of Map
- 3.3 Leveraging the Power of Map in Java 8
- 3.4 Exploring the Benefits of Map
- 3.5 Navigating Common Queries about Map
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Map Usage
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Deep Dive into Java 8’s Map
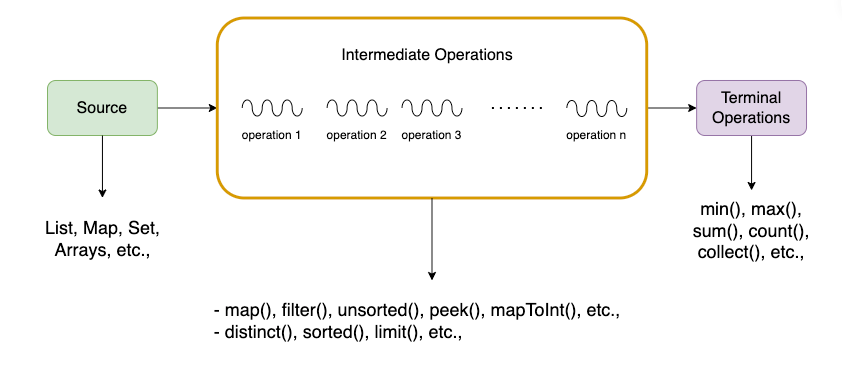
Java 8 marked a significant evolution in the language, introducing powerful features that streamlined development and enhanced code readability. Among these, the Map interface stands out as a cornerstone for storing and managing key-value pairs, offering a versatile and efficient mechanism for representing data relationships.
This article delves into the depths of Map in Java 8, exploring its core functionalities, exploring its benefits, and addressing common queries. We will navigate through the intricacies of this powerful data structure, highlighting its significance in modern Java development.
Understanding the Essence of Map
At its core, a Map is a data structure that associates keys with corresponding values. This key-value pairing forms the basis of its functionality, enabling efficient retrieval of values based on their associated keys. The keys within a Map must be unique, ensuring that each value can be accessed unambiguously.
Java 8 offers a rich collection of Map implementations, each tailored to specific use cases:
-
HashMap: This implementation is based on a hash table, providing fast access to elements. It is the most commonly used
Mapdue to its speed and efficiency. - TreeMap: This implementation utilizes a tree-based structure, offering sorted key-value pairs. It is ideal for scenarios requiring ordered traversal or retrieval of elements.
- LinkedHashMap: This implementation maintains the insertion order of elements, making it suitable for situations where preserving the sequence of entries is crucial.
- ConcurrentHashMap: Designed for multi-threaded environments, this implementation provides thread-safe access to elements, ensuring data consistency in concurrent operations.
Exploring the Key Features of Map
The Map interface in Java 8 provides a comprehensive set of methods for managing key-value pairs, enabling efficient data manipulation and retrieval. Some key features include:
-
put(key, value): This method inserts a new key-value pair into the
Map. If the key already exists, its associated value is replaced with the new value. -
get(key): This method retrieves the value associated with a given key. If the key is not found, it returns
null. - remove(key): This method removes the key-value pair associated with the provided key.
-
containsKey(key): This method checks if a key exists in the
Map. -
containsValue(value): This method checks if a value exists in the
Map. -
isEmpty(): This method determines if the
Mapis empty. -
size(): This method returns the number of key-value pairs in the
Map. -
keySet(): This method returns a
Setcontaining all the keys in theMap. -
values(): This method returns a
Collectioncontaining all the values in theMap. -
entrySet(): This method returns a
Setcontaining all the key-value pairs asMap.Entryobjects.
Leveraging the Power of Map in Java 8
The Map interface in Java 8 empowers developers to create robust and efficient data structures. Here are some key scenarios where Map shines:
-
Data Storage and Retrieval:
Mapprovides a natural way to store and retrieve data associated with specific keys. This is particularly useful for representing configurations, user profiles, or any data that requires key-based access. -
Caching:
Mapcan be effectively used to implement caching mechanisms, storing frequently accessed data for faster retrieval. -
Mapping Relationships:
Mapis ideal for representing relationships between entities, such as mapping employee IDs to their respective departments or customer names to their purchase history. -
Graph Representation:
Mapcan be utilized to represent graphs, where keys represent nodes and values represent their connecting edges. -
Data Aggregation:
Mapcan facilitate data aggregation, grouping data based on specific criteria and storing the aggregated results.
Exploring the Benefits of Map
The Map interface offers several advantages for developers:
-
Efficiency:
Mapimplementations, particularlyHashMap, provide efficient access to data based on keys, enabling quick retrieval and manipulation of information. -
Flexibility:
Mapallows for storing diverse data types, offering flexibility in representing relationships and managing data. -
Organization:
Mapenables structured data storage, organizing information based on key-value pairs, enhancing code readability and maintainability. -
Versatility:
Mapfinds applications in various domains, including data management, caching, graph representation, and more.
Navigating Common Queries about Map
Q1: What is the difference between HashMap and TreeMap?
A1: HashMap uses a hash table for storage, providing fast access to elements but not maintaining order. TreeMap utilizes a tree-based structure, offering sorted key-value pairs and ordered traversal.
Q2: How do I iterate over the elements in a Map?
A2: You can iterate over the key-value pairs using the entrySet() method. For example:
Map<String, Integer> myMap = new HashMap<>();
// ... populate the map ...
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : myMap.entrySet())
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
// ... process the key-value pair ...
Q3: How do I handle null keys or values in a Map?
A3: HashMap allows null keys and values, but other implementations may have restrictions. It is crucial to handle null values appropriately during retrieval and processing.
Q4: How do I create a Map with specific initial values?
A4: You can use the put() method to add initial key-value pairs during the Map creation. Alternatively, you can use the of() method introduced in Java 9 to create an immutable Map with specific values.
Q5: How do I use Map in a multi-threaded environment?
A5: Use ConcurrentHashMap for thread-safe access to Map data. It provides mechanisms to handle concurrent operations and ensure data consistency.
Tips for Effective Map Usage
-
Choose the Right Implementation: Select the
Mapimplementation that best suits your needs based on performance requirements, ordering needs, and concurrency considerations. - Handle Null Values: Be mindful of null keys and values, implementing appropriate checks and handling mechanisms.
-
Utilize Stream Operations: Java 8’s stream operations offer powerful tools for manipulating and processing data within
Map. - Optimize for Performance: Consider using efficient key hashing functions and appropriate data structures to optimize performance for large datasets.
-
Understand Thread Safety: If using
Mapin a multi-threaded environment, ensure thread safety by choosing appropriate implementations and employing synchronization mechanisms.
Conclusion
The Map interface in Java 8 stands as a powerful tool for managing key-value pairs, offering efficiency, flexibility, and versatility. Its wide range of implementations caters to diverse use cases, enabling developers to represent data relationships, implement caching mechanisms, and perform data aggregation tasks. Understanding the nuances of Map and its various implementations empowers developers to create robust and efficient data structures, enhancing the overall quality and performance of their Java applications.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Deep Dive into Java 8’s Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Geographical Journey Through The Republic Of Congo: Unveiling A Nation’s Landscape And Potential
- Navigating Iowa’s Roads: A Comprehensive Guide To The Iowa DOT Road Condition Map
- Navigating Moreno Valley: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Layout
- The Power Of Maps: Understanding The Role Of Map Servers In The Digital Age
- Mastering The Battle Royale: The Importance Of Warm-Up Maps In Fortnite
- A Comprehensive Guide To Printable State Maps: Unveiling The Power Of Visualization
- The Missouri River: A Vital Lifeline Across The American Heartland
- Deciphering Nevada’s Political Landscape: A Guide To The Silver State’s Electoral Map
Leave a Reply