Navigating The Labyrinth Of Thought: A Guide To Thought Mapping
Navigating the Labyrinth of Thought: A Guide to Thought Mapping
Related Articles: Navigating the Labyrinth of Thought: A Guide to Thought Mapping
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Labyrinth of Thought: A Guide to Thought Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Labyrinth of Thought: A Guide to Thought Mapping
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Labyrinth of Thought: A Guide to Thought Mapping
- 3.1 The Essence of Thought Mapping
- 3.2 The Benefits of Embracing Thought Mapping
- 3.3 The Mechanics of Thought Mapping
- 3.4 Thought Mapping in Action: Real-World Applications
- 3.5 FAQs about Thought Mapping
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Thought Mapping
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Power of Visual Thinking
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Labyrinth of Thought: A Guide to Thought Mapping

In the realm of human cognition, the ability to organize, analyze, and synthesize information is paramount. Thought mapping, a visual tool for structuring and representing information, offers a powerful means to navigate the labyrinth of our thoughts. This technique, also known as mind mapping, harnesses the power of visual representation to unlock clarity, enhance creativity, and foster a deeper understanding of complex ideas.
The Essence of Thought Mapping
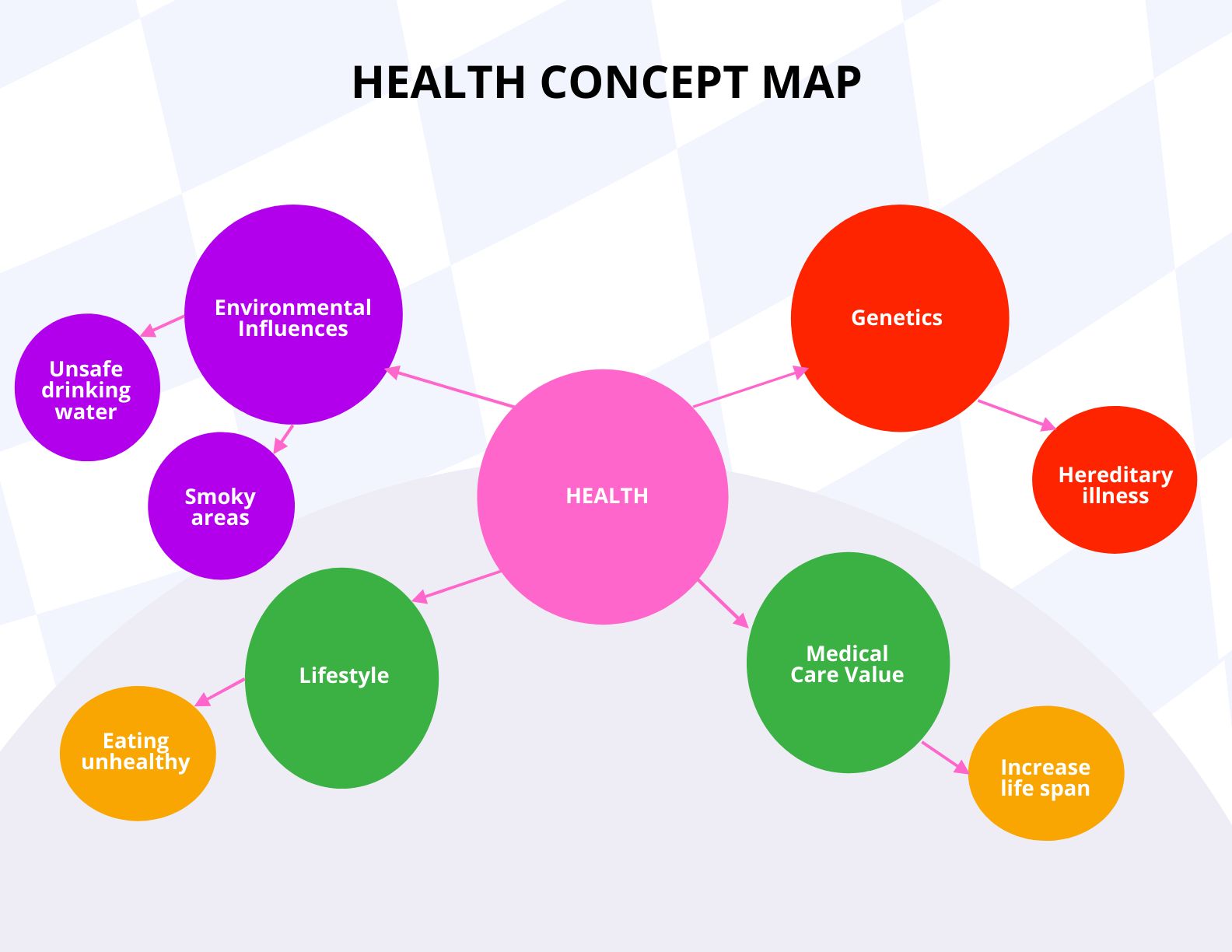
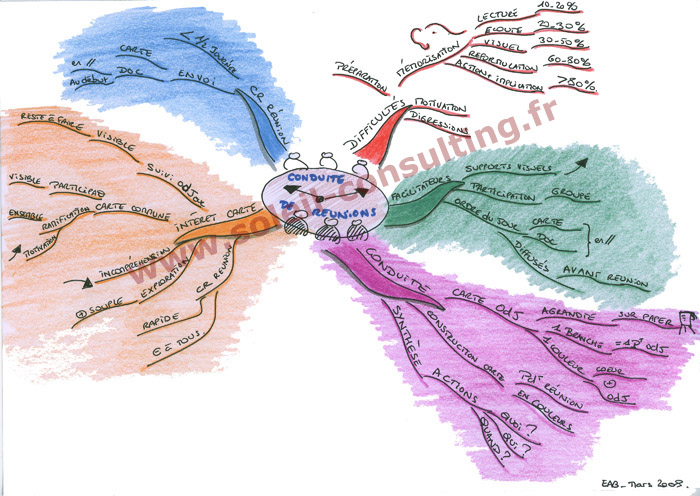
At its core, thought mapping is a method for capturing ideas, concepts, and relationships in a hierarchical and radial structure. The central idea or topic is placed at the center of the map, serving as the nucleus from which branches of related information radiate outward. These branches, representing key themes, concepts, or subtopics, are connected to the central idea through lines, forming a visually engaging network of information.
Key Characteristics of Thought Mapping:
- Non-linear Structure: Unlike traditional linear note-taking, thought mapping embraces a non-linear approach, allowing for the free flow of ideas and connections.
- Visual Representation: The use of colors, symbols, images, and keywords creates a visually appealing and memorable representation of information.
- Hierarchical Organization: Ideas are arranged in a hierarchical manner, with the main topic at the center and related subtopics branching out.
- Association and Connection: Thought mapping encourages the exploration of connections and relationships between ideas, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
The Benefits of Embracing Thought Mapping
Beyond its visual appeal, thought mapping offers a plethora of benefits, making it an invaluable tool for individuals across various domains:
- Enhanced Memory and Recall: The visual nature of thought maps engages both hemispheres of the brain, enhancing memory retention and facilitating recall.
- Improved Creativity and Innovation: The non-linear structure of thought maps encourages divergent thinking, promoting the generation of new ideas and fostering creative problem-solving.
- Effective Brainstorming and Idea Generation: Thought mapping provides a structured framework for brainstorming, enabling individuals to capture and organize a wide range of ideas.
- Clearer Communication and Presentation: Thought maps serve as powerful visual aids for communicating complex ideas, enhancing comprehension and engagement during presentations.
- Enhanced Learning and Comprehension: By visualizing information, thought mapping aids in the understanding and retention of complex concepts.
- Stress Reduction and Focus: The act of creating a thought map can be a calming and focused activity, reducing stress and improving concentration.
The Mechanics of Thought Mapping
Creating a thought map is a straightforward process that can be adapted to suit individual preferences and needs. The following steps provide a general framework:
- Identify the Central Topic: Begin by clearly defining the central topic or idea that you wish to explore.
- Create the Central Node: Place the central topic in the center of a blank page, representing the nucleus of your map.
- Generate Main Branches: Identify the primary themes or subtopics related to the central topic. Write these on branches radiating outwards from the central node.
- Develop Sub-Branches: For each main branch, identify related subtopics or supporting ideas. Write these on sub-branches that extend from the main branches.
- Use Keywords and Images: Employ concise keywords and relevant images to represent ideas and concepts on the branches.
- Connect Ideas with Lines: Connect related branches with lines, indicating relationships and connections between ideas.
- Use Colors and Symbols: Incorporate colors and symbols to highlight key information, differentiate categories, and enhance visual appeal.
Thought Mapping in Action: Real-World Applications
Thought mapping finds application in a diverse array of fields, proving its versatility and effectiveness across various contexts:
- Education: Thought mapping is a valuable tool for students, aiding in note-taking, studying, and exam preparation.
- Business: Companies utilize thought mapping for brainstorming, problem-solving, project planning, and strategic decision-making.
- Personal Development: Individuals employ thought mapping for goal setting, personal reflection, and developing self-awareness.
- Creative Arts: Writers, artists, and musicians use thought mapping to generate ideas, develop storylines, and explore creative concepts.
- Research and Development: Researchers utilize thought mapping to organize literature reviews, synthesize findings, and develop research proposals.
FAQs about Thought Mapping
1. What are the best tools for creating thought maps?
A wide range of tools are available, both digital and analog, to facilitate thought mapping. Popular digital options include mind mapping software such as MindNode, XMind, and FreeMind. For analog approaches, simple paper and pen are sufficient.
2. How can I improve my thought mapping skills?
Practice is key to improving your thought mapping skills. Start with simple topics and gradually move towards more complex ideas. Experiment with different styles and layouts to find what works best for you.
3. Is there a right or wrong way to create a thought map?
Thought mapping is a flexible technique, and there is no single "correct" way to create a map. The key is to find a method that works effectively for you and allows you to capture and organize information in a clear and meaningful way.
4. Can thought mapping be used for collaborative projects?
Yes, thought mapping can be a valuable tool for collaborative projects. Digital mind mapping software often includes features for real-time collaboration, allowing multiple individuals to contribute to the same map.
5. How can I effectively use thought maps for presentations?
Thought maps can be used as visual aids during presentations, enhancing engagement and clarity. Simplify the map for presentation purposes, focusing on key ideas and connections.
Tips for Effective Thought Mapping
- Start Simple: Begin with a central topic and gradually expand your map as you explore related ideas.
- Use Keywords: Employ concise keywords to represent concepts and ideas on the branches.
- Incorporate Visuals: Use images, symbols, and colors to enhance visual appeal and memory retention.
- Don’t Overthink: Allow your thoughts to flow freely and embrace the non-linear nature of thought mapping.
- Review and Refine: Once you have completed a map, review it and make adjustments as needed.
- Experiment with Different Styles: Explore various layout styles and techniques to find what works best for you.
Conclusion: The Power of Visual Thinking
Thought mapping, with its emphasis on visual representation and non-linear organization, provides a powerful framework for navigating the complexities of human thought. By harnessing the power of visualization, this technique unlocks clarity, enhances creativity, and fosters a deeper understanding of information. Whether employed for personal reflection, academic pursuits, or professional endeavors, thought mapping offers a versatile and effective tool for organizing ideas, stimulating innovation, and promoting effective communication. In a world saturated with information, the ability to visualize and synthesize knowledge through thought mapping emerges as a vital skill for navigating the labyrinth of our thoughts and achieving clarity in an increasingly complex world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Labyrinth of Thought: A Guide to Thought Mapping. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Geographical Journey Through The Republic Of Congo: Unveiling A Nation’s Landscape And Potential
- Navigating Iowa’s Roads: A Comprehensive Guide To The Iowa DOT Road Condition Map
- Navigating Moreno Valley: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Layout
- The Power Of Maps: Understanding The Role Of Map Servers In The Digital Age
- Mastering The Battle Royale: The Importance Of Warm-Up Maps In Fortnite
- A Comprehensive Guide To Printable State Maps: Unveiling The Power Of Visualization
- The Missouri River: A Vital Lifeline Across The American Heartland
- Deciphering Nevada’s Political Landscape: A Guide To The Silver State’s Electoral Map

Leave a Reply