Mapping The Legacy: The Olmec Civilization And Its Enduring Influence
Mapping the Legacy: The Olmec Civilization and its Enduring Influence
Related Articles: Mapping the Legacy: The Olmec Civilization and its Enduring Influence
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Legacy: The Olmec Civilization and its Enduring Influence. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Legacy: The Olmec Civilization and its Enduring Influence
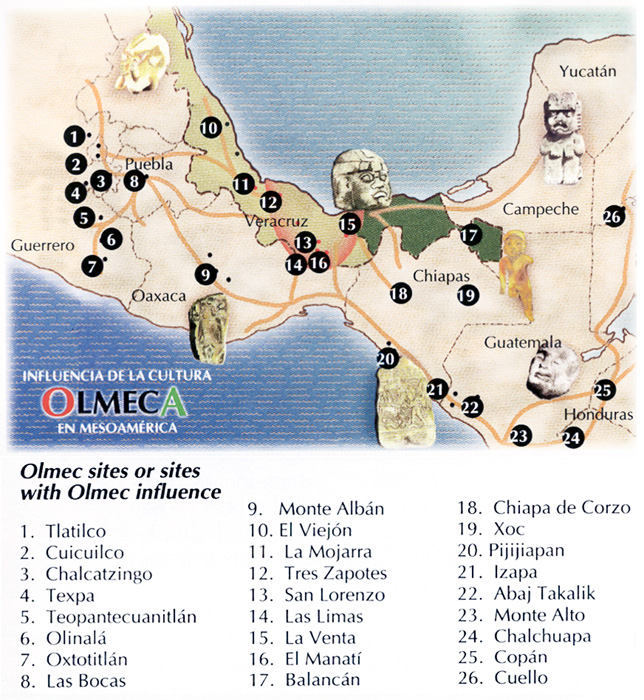
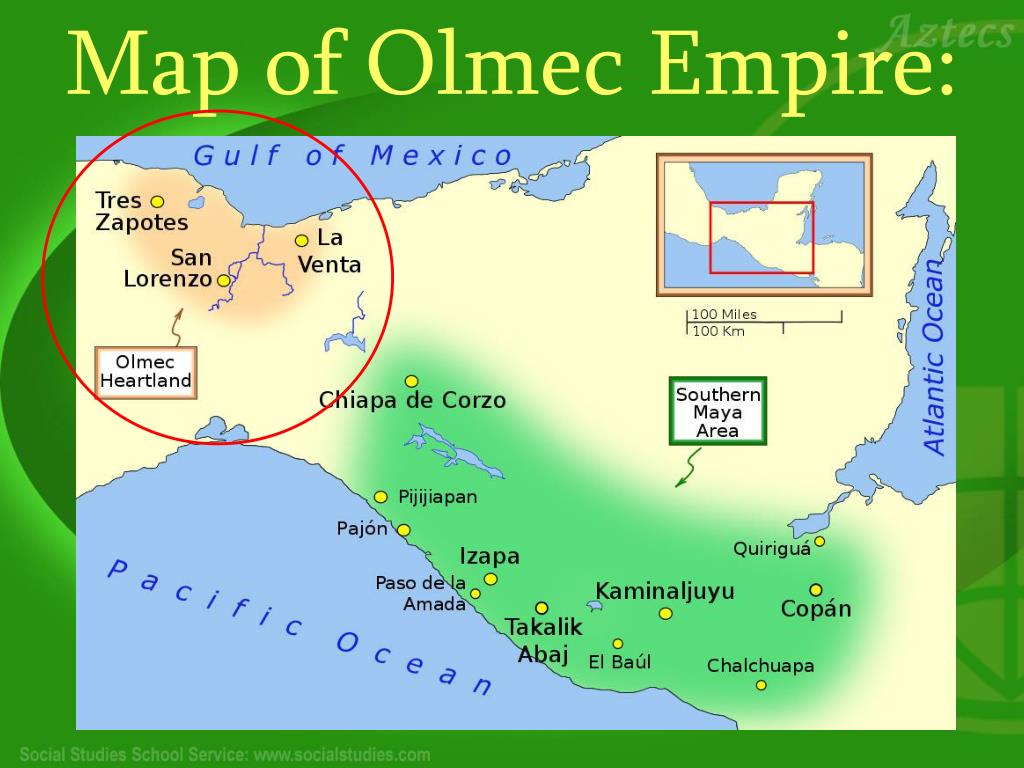
The Olmec civilization, flourishing in Mesoamerica between 1600 and 400 BCE, is often referred to as the "mother culture" of Mesoamerica. This designation stems from the profound impact the Olmec had on subsequent civilizations, leaving behind a rich legacy of artistic, religious, and societal innovations that reverberated throughout the region for centuries. Understanding the Olmec civilization requires a spatial perspective, a journey through the landscape they inhabited, and the intricate web of cultural exchanges they fostered. This journey begins with a comprehensive exploration of the Olmec civilization map.
The Olmec Heartlands: A Network of Power and Influence
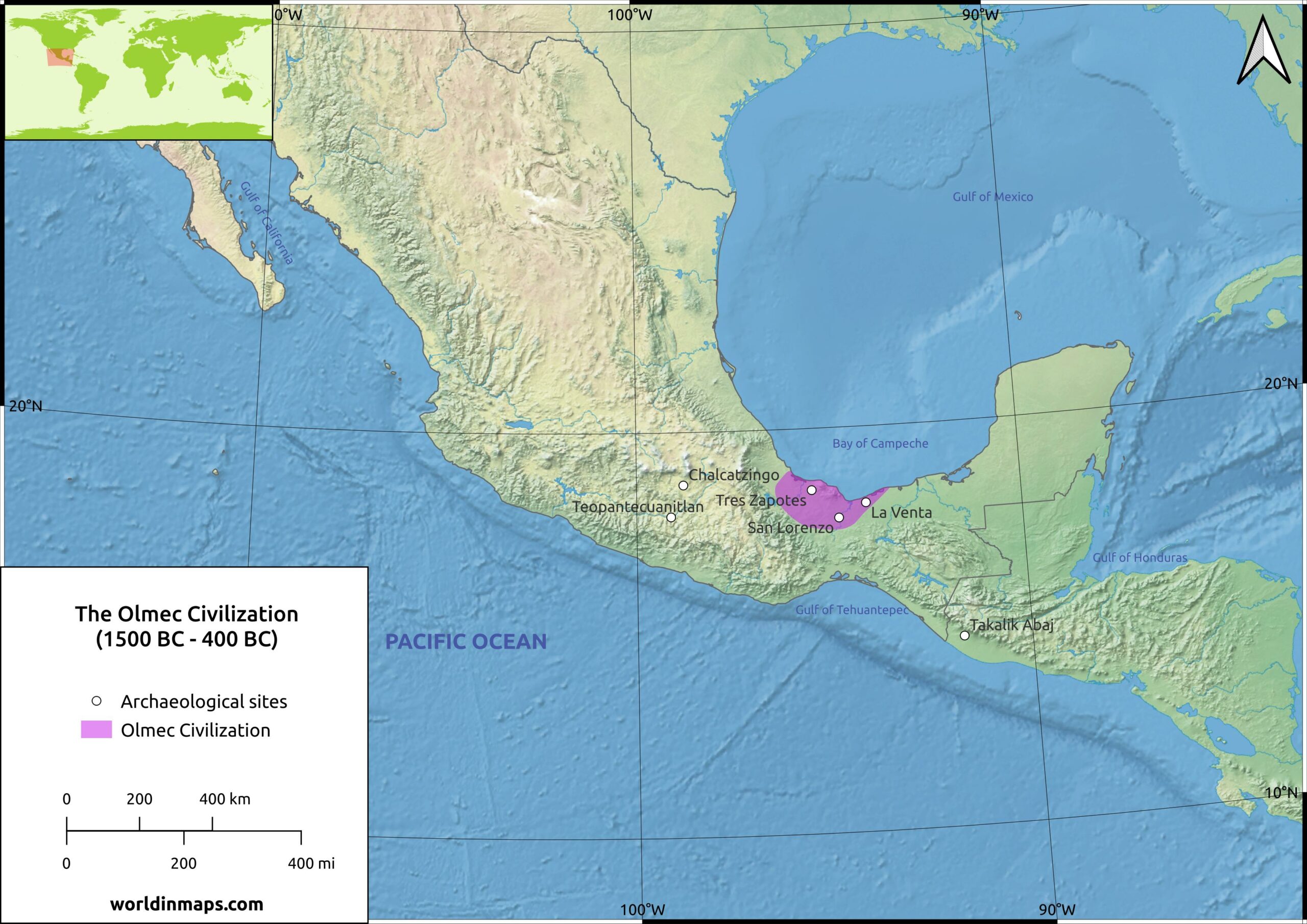
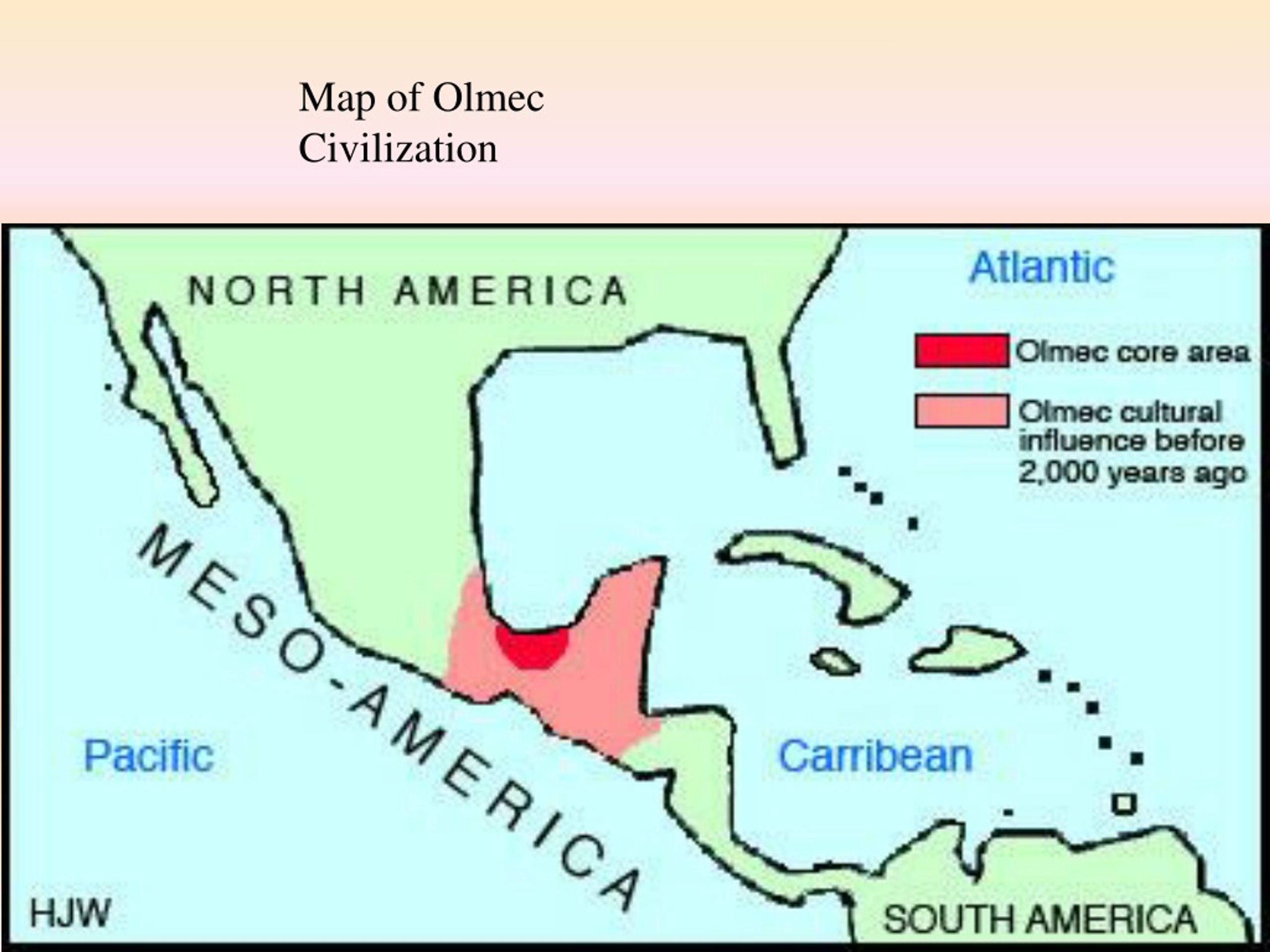
The Olmec civilization did not possess a unified, centralized empire in the traditional sense. Instead, their power was distributed across a network of interconnected settlements, each with its own unique character and significance. This network, often referred to as the "Olmec heartland," encompassed a vast region spanning the Gulf Coast of Mexico, from the modern-day states of Veracruz to Tabasco.
Key Sites and Their Significance:
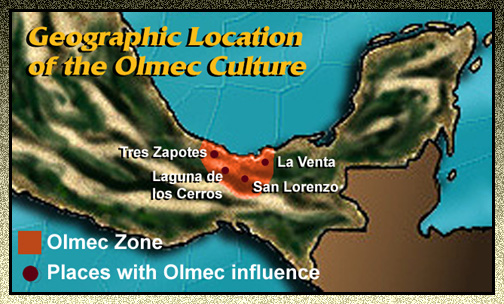
- San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán: Located in the present-day state of Veracruz, San Lorenzo was the earliest major Olmec center and served as a focal point for the civilization’s cultural development. It was here that the iconic Olmec colossal heads were sculpted, along with other impressive monumental sculptures and architecture.
- La Venta: Situated in Tabasco, La Venta emerged as a prominent Olmec center around 900 BCE. The site is renowned for its massive pyramid, intricately carved jade objects, and a complex system of drainage canals, indicating a sophisticated level of urban planning.
- Tres Zapotes: Located in Veracruz, Tres Zapotes played a pivotal role in the later stages of Olmec civilization. The site is known for its monumental sculptures, including the "Tres Zapotes Stela," which features the earliest known Mesoamerican calendar inscription.
- Laguna de los Cerros: Located in Tabasco, Laguna de los Cerros is considered one of the earliest Olmec settlements, dating back to the 16th century BCE. The site provides valuable insights into the origins and development of the Olmec civilization.
The Map as a Tool for Understanding:
The Olmec civilization map provides a crucial framework for understanding the spatial dynamics of this ancient society. It reveals the strategic location of key settlements, the interconnectedness of the Olmec heartland, and the geographical factors that influenced their development. By studying the map, researchers can gain insights into:
- Trade and Communication: The Olmec heartland was a hub of trade and communication, with settlements strategically located along trade routes and waterways. The map reveals the intricate network of exchange that connected Olmec communities and facilitated the spread of cultural ideas and innovations.
- Political and Social Organization: The distribution of settlements and the presence of monumental architecture suggest a complex system of political and social organization. The map helps to decipher the hierarchy of power within the Olmec civilization and the roles played by different settlements.
- Environmental Adaptations: The Olmec civilization flourished in a diverse environment, ranging from coastal lowlands to mountainous regions. The map highlights the environmental factors that influenced Olmec settlement patterns and the adaptations they developed to thrive in their unique landscape.
Beyond the Heartlands: The Olmec Influence
The Olmec civilization’s influence extended far beyond their heartland, leaving an indelible mark on subsequent Mesoamerican cultures. This influence is evident in the widespread adoption of Olmec artistic motifs, religious beliefs, and societal structures by later civilizations. The Olmec map serves as a vital tool for understanding the spread of these cultural elements.
- The Rise of the Maya: The Maya civilization, which flourished in the Yucatan Peninsula and surrounding regions, inherited many Olmec cultural traits, including the use of a sophisticated calendar system, hieroglyphic writing, and the concept of rulership based on divine ancestry.
- The Teotihuacan Influence: The Teotihuacan civilization, which rose to prominence in central Mexico, also borrowed heavily from Olmec traditions. The Teotihuacan pyramids, for example, bear a striking resemblance to the monumental architecture found at La Venta.
- The Zapotec and Mixtec Legacy: The Zapotec and Mixtec civilizations, which thrived in Oaxaca, were also influenced by Olmec culture, adopting their artistic styles and religious practices.
The Olmec Legacy: A Foundation for Mesoamerican Civilization
The Olmec civilization map reveals a complex and dynamic society that played a pivotal role in shaping the course of Mesoamerican history. The Olmec legacy, evident in the cultural innovations and societal structures they developed, served as a foundation upon which subsequent civilizations built their own unique identities.
FAQs about the Olmec Civilization Map:
1. What are the main features of the Olmec civilization map?
The Olmec civilization map highlights the network of settlements in the Olmec heartland, including key sites like San Lorenzo, La Venta, Tres Zapotes, and Laguna de los Cerros. It reveals the strategic location of these settlements, their interconnectedness, and the geographical factors that influenced their development.
2. How does the Olmec civilization map contribute to our understanding of their trade and communication?
The map reveals the strategic location of Olmec settlements along trade routes and waterways, indicating a complex system of trade and communication that connected communities throughout the Olmec heartland.
3. How does the Olmec civilization map help us understand their political and social organization?
The distribution of settlements and the presence of monumental architecture suggest a complex system of political and social organization. The map helps to decipher the hierarchy of power within the Olmec civilization and the roles played by different settlements.
4. What is the significance of the Olmec civilization map in terms of environmental adaptations?
The map highlights the diverse environment inhabited by the Olmec civilization, from coastal lowlands to mountainous regions. It reveals the environmental factors that influenced Olmec settlement patterns and the adaptations they developed to thrive in their unique landscape.
5. How does the Olmec civilization map illustrate the influence of Olmec culture on later civilizations?
The map demonstrates the geographical extent of Olmec influence, revealing how their artistic motifs, religious beliefs, and societal structures spread to other regions and influenced the development of subsequent Mesoamerican cultures.
Tips for Understanding the Olmec Civilization Map:
- Focus on the Key Sites: Identify the main settlements within the Olmec heartland and understand their significance in terms of political, economic, and cultural development.
- Consider the Geographical Context: Analyze the location of settlements in relation to trade routes, waterways, and natural resources.
- Explore the Connections: Understand how different Olmec settlements were interconnected and how trade and communication networks facilitated cultural exchange.
- Look for Evidence of Influence: Identify the ways in which Olmec culture spread beyond their heartland and influenced subsequent civilizations.
- Engage with the Map as a Tool: Use the map as a starting point for further research and exploration, seeking out additional information about specific sites, cultural practices, and the broader context of Olmec civilization.
Conclusion:
The Olmec civilization map is not merely a static representation of geographical locations. It is a window into a complex and dynamic society that shaped the course of Mesoamerican history. By studying the map, we gain a deeper understanding of the Olmec civilization’s spatial dynamics, their trade and communication networks, their political and social organization, and their enduring influence on subsequent cultures. The map serves as a vital tool for exploring the rich tapestry of Olmec civilization, a civilization that continues to inspire awe and fascination centuries after its demise.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Legacy: The Olmec Civilization and its Enduring Influence. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Geographical Journey Through The Republic Of Congo: Unveiling A Nation’s Landscape And Potential
- Navigating Iowa’s Roads: A Comprehensive Guide To The Iowa DOT Road Condition Map
- Navigating Moreno Valley: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Layout
- The Power Of Maps: Understanding The Role Of Map Servers In The Digital Age
- Mastering The Battle Royale: The Importance Of Warm-Up Maps In Fortnite
- A Comprehensive Guide To Printable State Maps: Unveiling The Power Of Visualization
- The Missouri River: A Vital Lifeline Across The American Heartland
- Deciphering Nevada’s Political Landscape: A Guide To The Silver State’s Electoral Map
Leave a Reply