Mapping The Invisible Enemy: Understanding Tick-Borne Disease Risk
Mapping the Invisible Enemy: Understanding Tick-Borne Disease Risk
Related Articles: Mapping the Invisible Enemy: Understanding Tick-Borne Disease Risk
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Invisible Enemy: Understanding Tick-Borne Disease Risk. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Invisible Enemy: Understanding Tick-Borne Disease Risk
Ticks, tiny arachnids often overlooked, pose a significant threat to human and animal health. These parasitic creatures can transmit a variety of diseases, some of which can be debilitating or even fatal. To effectively combat this invisible enemy, understanding the geographic distribution of ticks and the diseases they carry is crucial. This is where tick maps come into play.
Tick Maps: A Visual Guide to Risk
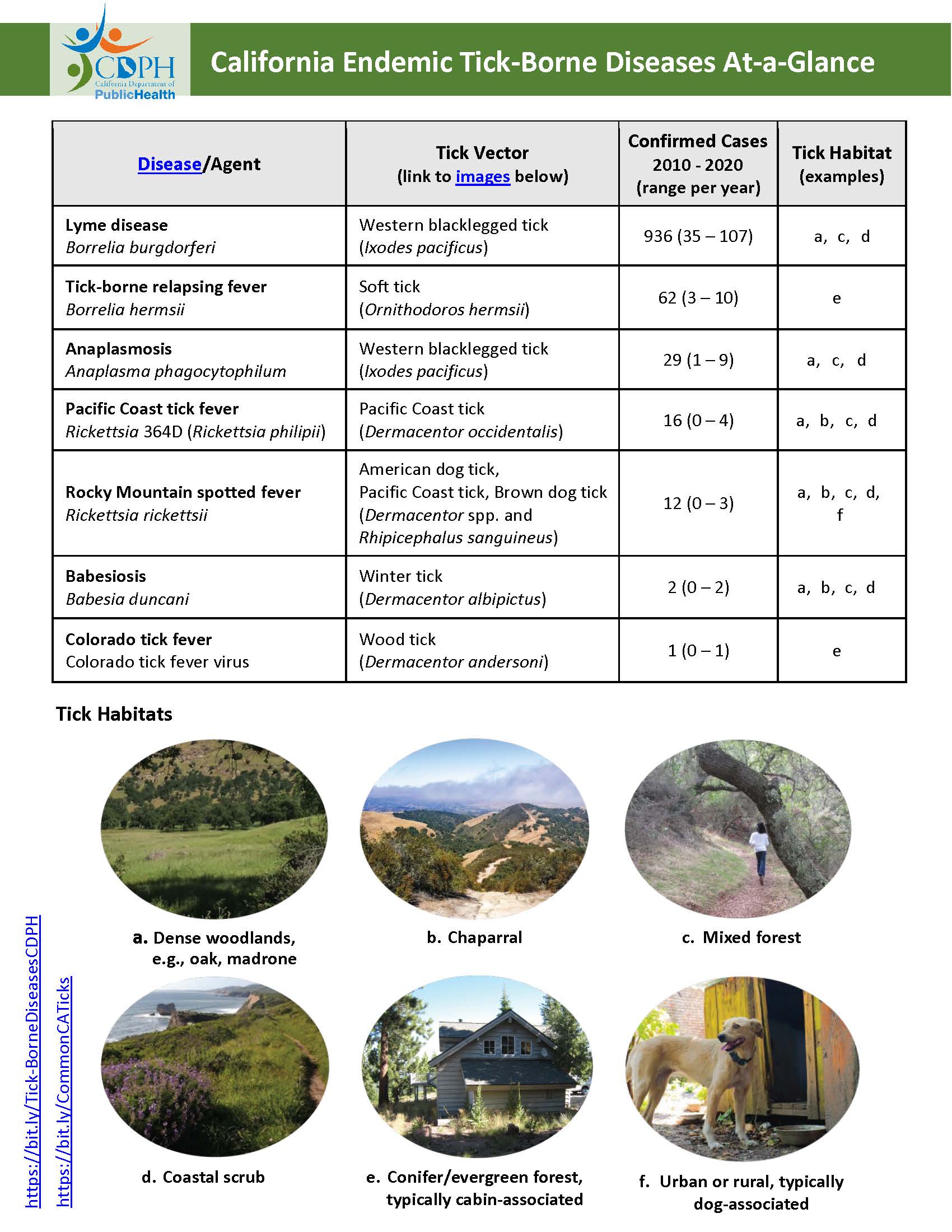
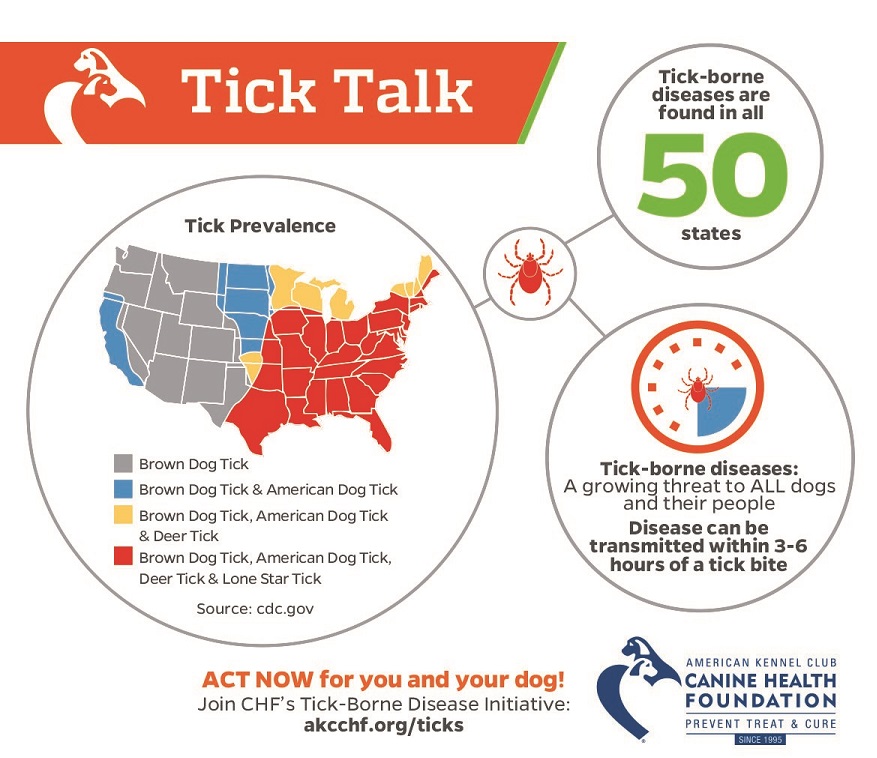
A tick map, also known as a tick distribution map, is a visual representation of the geographical spread of different tick species and the diseases they transmit. These maps are essential tools for:
- Public Health Officials: Identifying areas with high tick populations and disease prevalence allows for targeted prevention campaigns, surveillance programs, and resource allocation.
- Healthcare Professionals: Understanding the local tick species and associated diseases helps in diagnosis, treatment, and patient education.
- Individuals: Tick maps empower individuals to make informed decisions about outdoor activities, personal protective measures, and seeking timely medical attention.
Understanding the Data: A Comprehensive View
Tick maps are not simply static representations of tick presence. They are complex data visualizations that integrate various sources of information, including:
- Tick Surveillance Data: This data is collected through active surveillance programs where ticks are collected and analyzed for the presence of pathogens.
- Disease Reporting Data: Reports of confirmed cases of tick-borne diseases provide valuable insights into the geographic distribution of specific illnesses.
- Environmental Data: Factors like climate, vegetation, and animal populations play a significant role in tick distribution. This data is incorporated into tick maps to provide a more nuanced understanding of risk.
- Citizen Science Data: Public participation through platforms like iNaturalist and TickReport allows for citizen scientists to contribute observations of tick sightings, enriching the data pool.
Types of Tick Maps: Tailored to Specific Needs
Tick maps are not one-size-fits-all. They are tailored to meet specific needs and provide different levels of detail:
- National Level Maps: These maps provide a broad overview of tick distribution across a country, highlighting areas with high prevalence of specific tick species.
- Regional Level Maps: Maps focusing on specific states or regions provide more granular data on tick species and associated diseases within a smaller geographic area.
- Local Level Maps: These maps focus on specific localities, such as parks, hiking trails, or neighborhoods, providing detailed information on tick risk within a defined area.
Beyond the Map: Utilizing the Information
Tick maps are powerful tools, but their true value lies in their practical application. The information they provide can be utilized in various ways:
- Targeted Prevention Campaigns: Public health officials can use tick maps to target prevention campaigns in areas with high tick populations and disease prevalence. This includes promoting awareness about tick bites, providing information on tick-repellent measures, and educating the public about safe outdoor practices.
- Surveillance and Monitoring Programs: Tick maps can guide the deployment of surveillance programs to monitor tick populations and disease trends. This helps in early detection of outbreaks and the implementation of timely control measures.
- Risk Assessment for Individuals: Individuals can use tick maps to assess their risk of encountering ticks and contracting tick-borne diseases based on their location and activities. This information empowers them to take appropriate preventive measures, such as wearing protective clothing, using tick repellents, and performing regular tick checks.
- Research and Development: Tick maps provide valuable data for researchers studying tick ecology, disease transmission, and the development of new prevention and treatment strategies.
FAQs about Tick Maps
Q: What are the limitations of tick maps?
A: Tick maps are valuable tools but have limitations. They are based on available data, which may not be comprehensive or uniformly distributed. Additionally, tick populations and disease prevalence can fluctuate due to factors like climate change and animal movements.
Q: Are tick maps always accurate?
A: Tick maps are based on the best available data, but their accuracy can vary depending on the data sources and the level of detail provided. It’s important to consider the limitations of any map and consult with local health authorities for the most up-to-date information.
Q: Can I use tick maps to predict the exact location of ticks?
A: Tick maps indicate general areas of tick prevalence, but they cannot pinpoint the exact location of individual ticks. Tick populations can vary within a given area, and factors like microclimate and vegetation can influence their presence.
Q: Where can I find reliable tick maps?
A: Reliable tick maps are often provided by government agencies, public health organizations, and research institutions. Look for maps from trusted sources like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), state health departments, and universities.
Tips for Using Tick Maps
- Consult Multiple Sources: Compare information from different tick maps to get a comprehensive understanding of the risk in your area.
- Consider Local Factors: Remember that tick maps provide general information. Local factors, like specific trails or parks, can influence tick populations.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest information on tick-borne diseases and tick populations in your area.
- Practice Tick Prevention: Regardless of your location, always practice tick prevention measures, such as wearing protective clothing, using tick repellents, and conducting thorough tick checks.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Protection
Tick maps are essential tools for understanding the geographic distribution of ticks and the diseases they carry. They provide valuable information for public health officials, healthcare professionals, and individuals, empowering them to take proactive measures to prevent tick-borne diseases. By utilizing these maps and practicing effective tick prevention strategies, we can minimize the risk of these invisible enemies and protect ourselves and our loved ones from the potential consequences of tick-borne illnesses.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Invisible Enemy: Understanding Tick-Borne Disease Risk. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Geographical Journey Through The Republic Of Congo: Unveiling A Nation’s Landscape And Potential
- Navigating Iowa’s Roads: A Comprehensive Guide To The Iowa DOT Road Condition Map
- Navigating Moreno Valley: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Layout
- The Power Of Maps: Understanding The Role Of Map Servers In The Digital Age
- Mastering The Battle Royale: The Importance Of Warm-Up Maps In Fortnite
- A Comprehensive Guide To Printable State Maps: Unveiling The Power Of Visualization
- The Missouri River: A Vital Lifeline Across The American Heartland
- Deciphering Nevada’s Political Landscape: A Guide To The Silver State’s Electoral Map
Leave a Reply