A Mountainous Tapestry: Exploring The Geography Of Asia
A Mountainous Tapestry: Exploring the Geography of Asia
Related Articles: A Mountainous Tapestry: Exploring the Geography of Asia
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Mountainous Tapestry: Exploring the Geography of Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Mountainous Tapestry: Exploring the Geography of Asia

Asia, the largest and most populous continent, is a land of remarkable diversity. This diversity extends beyond its cultural and linguistic tapestry to its physical landscape, most notably its towering mountain ranges that have shaped its history, environment, and the lives of its inhabitants. Understanding the distribution and significance of these mountains is crucial to grasping the complex geography and dynamic nature of Asia.
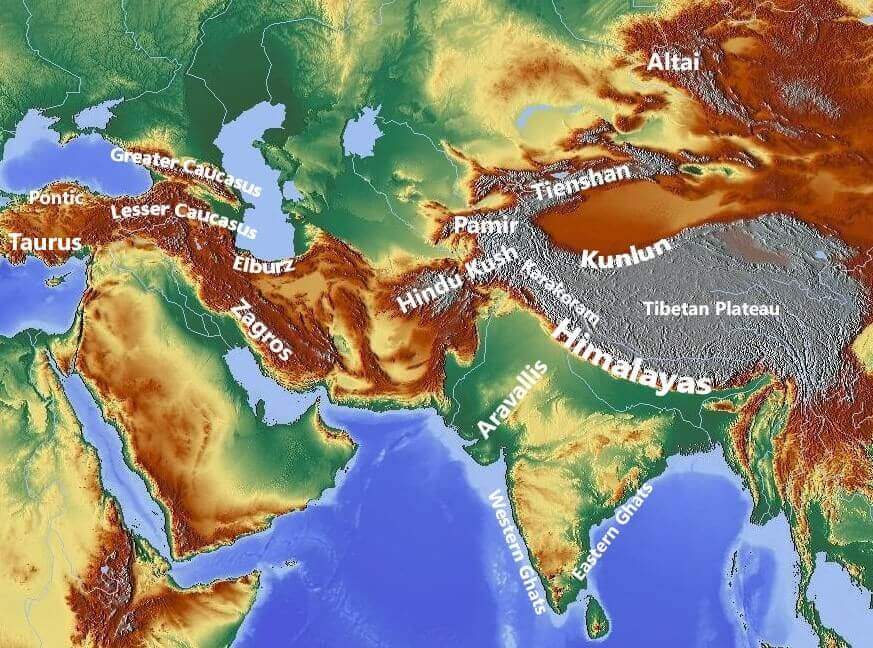
The Himalayan Giants: A Roof of the World
The Himalayas, often referred to as the "Roof of the World," are the most prominent mountain range in Asia. This colossal chain, spanning over 2,400 kilometers, encompasses the highest peaks on Earth, including Mount Everest, the world’s tallest. The Himalayas are not just a geographical feature; they are a vital ecological and cultural hub.
- Ecological Significance: The Himalayas act as a water tower, providing water to major rivers like the Ganges, Indus, and Brahmaputra, which sustain millions of people downstream. The mountains also harbor a rich biodiversity, with unique ecosystems and endemic species.
- Cultural Influence: The Himalayas have played a significant role in shaping the cultures and religions of the region. Tibetan Buddhism, for example, has deep roots in the Himalayan region, while the mountains have also inspired numerous myths and legends.
Beyond the Himalayas: Diverse Mountain Ranges
Asia is home to a vast array of other mountain ranges, each with its distinct characteristics and importance.
- The Hindu Kush: This range, located in Central Asia, forms a natural boundary between Afghanistan and Pakistan. It is known for its rugged terrain, which has historically made it difficult to traverse, and its role in shaping the region’s geopolitics.
- The Karakoram: This range, located in the north of the Himalayas, is home to some of the world’s highest peaks, including K2, the second-highest mountain in the world. The Karakoram is also known for its vast glaciers, which are a vital source of water for the region.
- The Tian Shan: This range, located in Central Asia, stretches across parts of China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Uzbekistan. It is known for its diverse landscapes, including alpine meadows, forests, and glaciers. The Tian Shan is also home to a number of important cultural and historical sites.
- The Altai Mountains: This range, located in Central Asia, stretches across parts of Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan. It is known for its rugged terrain, which has historically made it difficult to traverse, and its role in shaping the region’s geopolitics.
The Impact of Mountains on Asia’s Geography
The mountain ranges of Asia have profoundly impacted the continent’s geography and environment.
- Climate Patterns: Mountains play a crucial role in influencing regional climate patterns. The Himalayas, for example, act as a barrier to moisture-laden winds, resulting in heavy rainfall on the south side and a dry, arid climate on the north side.
- River Systems: Mountains are the source of many of Asia’s major rivers, which provide water for agriculture, transportation, and hydropower. The Ganges, Indus, and Brahmaputra rivers, all originating in the Himalayas, are vital lifelines for millions of people.
- Biodiversity: Mountains are home to a wide range of ecosystems and species. The Himalayas, for example, are a global biodiversity hotspot, with a vast array of plants and animals found nowhere else.
- Resource Potential: Mountains are rich in natural resources, including minerals, timber, and hydropower. These resources have played a significant role in the economic development of many Asian countries.
Challenges and Opportunities
While mountains offer numerous benefits, they also pose challenges.
- Natural Disasters: Mountains are prone to natural disasters, including earthquakes, landslides, and floods. These events can have devastating consequences for the people and infrastructure in the region.
- Climate Change: Climate change is impacting the mountains of Asia, leading to glacial melt, changes in precipitation patterns, and increased risks of natural disasters.
- Development Challenges: Mountains are often remote and difficult to access, making it challenging to provide services and infrastructure to their inhabitants.
FAQs
Q: What are the highest mountains in Asia?
A: The highest mountains in Asia are located in the Himalayas, including Mount Everest, K2, Kangchenjunga, Lhotse, and Makalu.
Q: What is the significance of the Himalayas?
A: The Himalayas are a vital water source for major rivers, a global biodiversity hotspot, and a region with significant cultural and religious importance.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced by people living in mountainous regions?
A: People living in mountainous regions face challenges related to access to services, infrastructure, and natural disasters.
Tips for Exploring the Mountains of Asia
- Plan Ahead: Research the region you are planning to visit, including its climate, terrain, and potential hazards.
- Respect Local Cultures: Be mindful of local customs and traditions when traveling in mountainous regions.
- Be Prepared for Altitude: Acclimatize gradually to the altitude to avoid altitude sickness.
- Pack Appropriately: Pack warm clothing, sturdy footwear, and essential gear for hiking and camping.
- Consider a Guided Tour: Hiring a local guide can enhance your experience and ensure your safety.
Conclusion
The mountains of Asia are a testament to the continent’s remarkable diversity and dynamism. From the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the rugged ranges of Central Asia, these mountains have shaped the geography, environment, and cultures of the region. Understanding the role of mountains in Asia is crucial for appreciating the continent’s complex and fascinating landscape. As we continue to explore and learn from these majestic features, we gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of nature, culture, and human society.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Mountainous Tapestry: Exploring the Geography of Asia. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- A Geographical Journey Through The Republic Of Congo: Unveiling A Nation’s Landscape And Potential
- Navigating Iowa’s Roads: A Comprehensive Guide To The Iowa DOT Road Condition Map
- Navigating Moreno Valley: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Layout
- The Power Of Maps: Understanding The Role Of Map Servers In The Digital Age
- Mastering The Battle Royale: The Importance Of Warm-Up Maps In Fortnite
- A Comprehensive Guide To Printable State Maps: Unveiling The Power Of Visualization
- The Missouri River: A Vital Lifeline Across The American Heartland
- Deciphering Nevada’s Political Landscape: A Guide To The Silver State’s Electoral Map
Leave a Reply